Compliance And Certifications
Achieving Compliance, Earning Certifications, and Building Trust in Every Step
Home >> Compliance & Certifiactions
COMPLIANCE CRAFTED, CERTIFICATIONS EARNED
Your Journey to Assurance and Excellence
PCI DSS:
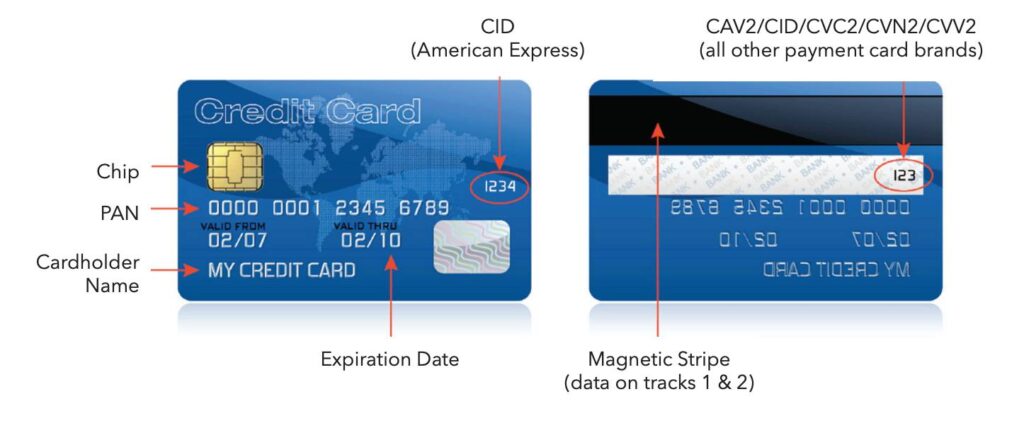
ByteGRC assists companies like yours to comply with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). It is a worldwide security standard that ensures the security of payment card data. If payment cards are one of the services provided by your company, then you will have to commit to the PCI DSS requirements in order to ensure safety and security in all your transactions.
PCI DSS was developed by leading card companies such as American Express, Discover, JCB, Mastercard, and Visa. The companies manage the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC) to look after these regulations
Being a certified Qualified Security Assessor (QSA), ByteGRC provides a vast array of services that are designed to assist enterprises with every PCI DSS demand and with the compliance to keep. We are there for our partners all the way to make the whole process easier and to ensure that they comply with all the requirements and secure the information of their customers.
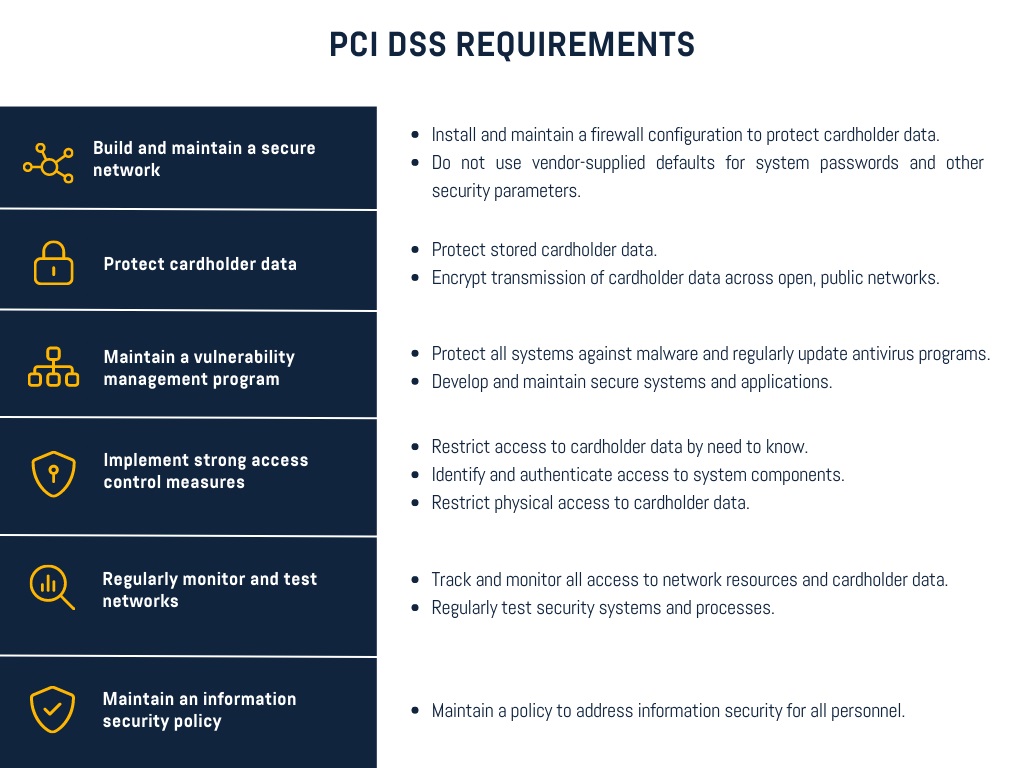
PCI DSS consists of a half dozen primary objectives and 12 particular measures to be observed by each company receiving card payments. Those requirements can comprise security systems, processes, and testing, etc., and are presented in such a way as to protect the cardholder. Conforming to the above requirements means adhering to the rules that are really deep down security by procedure in nature.
Our experienced team at ByteGRC helps businesses understand and meet all the PCI DSS requirements to get certified and stay protected.
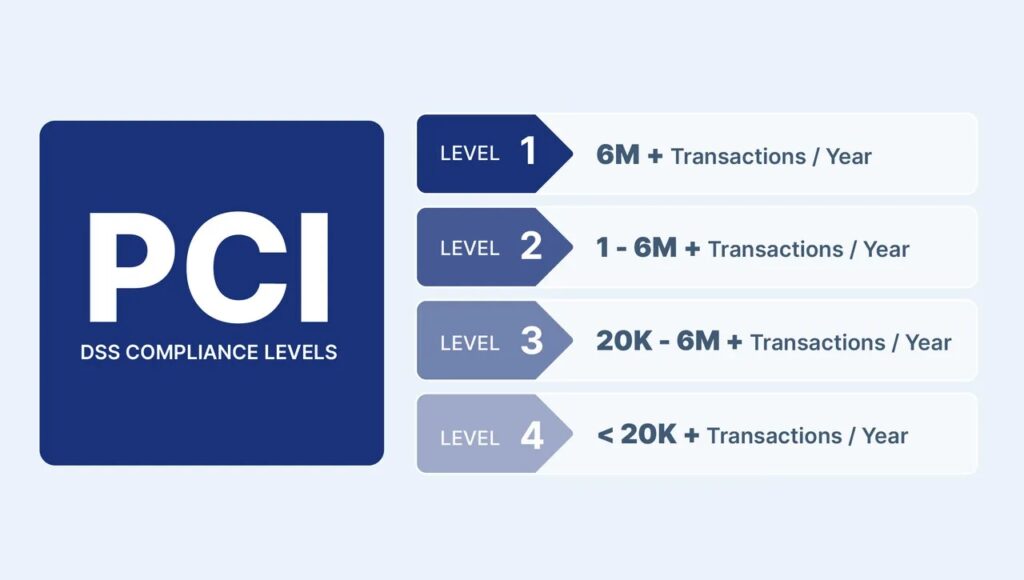
Our experts also help businesses prevent data breaches and fraud. We provide professional guidance on the right PCI DSS level for each business, depending on how many card transactions they handle each year.
Benefits of PCI DSS Certification
- Builds customer trust
- Helps avoid penalties
- Reduces security risks
- Meets other industry standards
SAMA Cyber Security Framework
Today, we often use online services that need to be safe and secure. Both businesses and people depend on these services. They are key to a strong digital economy and keeping the country safe. Trust in Saudi Arabia’s financial system relies on protecting private data.
With the advancements in technology, such as fintech and blockchain, it has become necessary to protect data from cyber threats. The financial industry is aware of the rapid development of these risks and of the necessity to be well prepared.
To support with this, SAMA came up with the Cyber Security Framework. SAMA has drawn up the Framework for financial institutions regulated by SAMA, the Member Organizations, which is aimed at making them capable of identifying and mitigating cyber security risks. Such organizations must adopt this Framework in the protection of their digital assets.
Goals of the Framework:
- To create a common approach for handling cyber security in Member Organizations.
- To ensure Member Organizations reach a strong level of cyber security.
- To make sure cyber security risks are managed properly in Member Organizations.
The Framework serves further goal of binary assessment of the Member Organizations’ capabilities with respect to cybersecurity, and their subsequent correlating of output with the performance of another set of organizations.
The Framework follows SAMA’s rules and international standards like NIST, ISF, ISO, BASEL, and PCI.
This framework replaces all older SAMA guidelines related to cybersecurity. For more details, see ‘Appendix A – Overview of previous SAMA guidelines.’
Saudi Data Management and Personal Data Protection Standards:
Saudi Data Management and Personal Data Protection Standard is, in general, a plan made to provide safety and appropriate supervision of data, whether the organizations are government-related or private establishments that operate on the basis of government.
With responsibility for data regulation in Saudi Arabia, the National Data Management Office (NDMO) formulated a standard for the purpose of guiding organizations in the implementation of data management and protection best practices.
The standard includes 15 key areas, with 77 controls and 191 specific guidelines. These guidelines are divided into three levels of priority (P1, P2, and P3), each with deadlines for implementation:

At ByteGRC, we provide expert services to help organizations meet these standards. Our team conducts a complete compliance assessment, measuring progress for each requirement. Fully completed guidelines receive a 100% rating, while incomplete ones are rated lower.
Our experts help clients by offering:
- Gap analysis to identify areas of improvement
- Risk assessments to understand potential threats
- Remediation planning to fix any gaps
- Documentation of policies
- Staff training
- Internal audits to ensure ongoing compliance
- Management reviews and successful final audits
At the end of the project, we deliver comprehensive reports and documents to help organizations continue to meet the standards.
ISO 27001
It is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) that put the ISO/IEC 27001 standard in place. This one is really important as it supports the security of a company’s information not only from the external risks the data could be subject to but also from the possibility of losing it. It serves the dual role of protecting the company’s information and proving its strong intention to safeguard the privacy of reliable sources.
ISO 27001 focuses on protecting important and sensitive information by setting up an Information Security Management System (ISMS). This system uses a risk-based approach and aims to build trust with clients, partners, and stakeholders.
The standard helps manage information security to:
- Meet legal requirements.
- Ensure information is confidential, intact, and available—known as the CIA principles.
CIA Principles:
- Only authorized people can access or change the information.
- Information must be accurate and trustworthy.
- Authorized users should be able to access the information whenever they need it, while keeping unauthorized users out.
ByteGRC helps many organizations get ISO 27001 certified. Our experts assist with:
- Analyzing gaps in current security practices.
- Assessing risks.
- Creating necessary policies and procedures.
- Developing the ISMS framework.
- Planning and implementing fixes.
- Supporting policy documentation.
- Training staff on ISO 27001.
- Conducting internal audits.
- Reviewing management processes.
- Ensuring a successful audit.
- Facilitating the certification process.
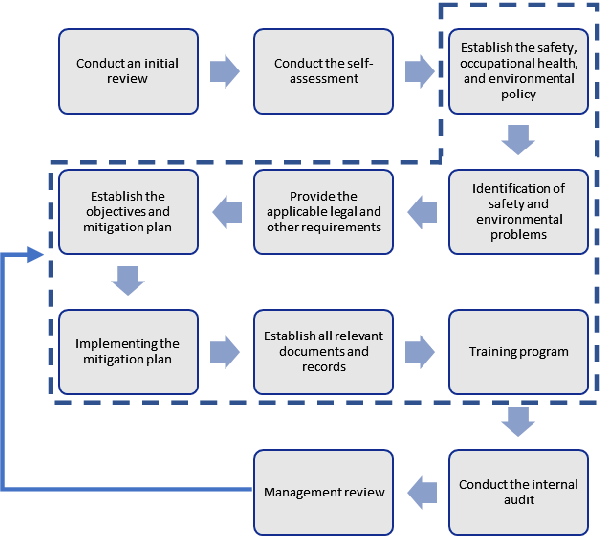
Action Plan
The steps for the ISO 27001 process are shown in the diagram below.
Benefits of ISO 27001:
- Builds trust and credibility, helping grow your business.
- Reduces the risk of fines or legal issues.
- Lowers the chance of security breaches caused by staff.
- Keeps information secure, allowing the business to run smoothly.
- Ensures information is protected and accessible.
- Enhances the organization’s reputation and boosts confidence.
- Works for organizations of any size.
- Saves money by reducing security incidents.
ISO/IEC 27017
ISO/IEC 27017:2015 is a set of guidelines for securing cloud services. It builds on ISO/IEC 27001:2013 and ISO/IEC 27002 by adding specific controls for cloud service providers and their customers. Organizations use these controls based on their specific needs.
- Shared responsibilities between cloud providers and customers
- Safe return of customer assets when contracts end
- Isolation of virtual environments
- Secure setup of virtual machines
- Documenting important operational procedures
- Allowing customers to monitor activities in the cloud
- Aligning security for virtual and physical networks
Benefits of ISO 27017 Certification

External assurance to customers
Gives customers confidence that their cloud data is secure.

Reduce Risk
Helps lower the chances of security breaches and boosts trust.

Enhances Certification
Builds on and improves existing ISO 27001 certification.

Framework for Cloud Customers
Provides a solid security framework for cloud customers and holds providers accountable.

Comprehensive Security Framework
Ensures a complete security framework for cloud services, enhancing provider accountability.
Why Implement ISO 27017?
ISO/IEC 27017 plays a very important role in the protection of your cloud data, which also minimizes the possibility of data breaches and leads to the establishment of customers’ trust. It provides a harmonized way of ensuring the security of cloud and offers a clear direction to clients on how to manage their cloud service providers.
The standard includes guidelines on asset management, secure handling of customer data, and maintaining isolation of virtual environments. With cloud data breaches becoming more common, implementing ISO/IEC 27017 ensures you’re doing everything possible to protect your data.
Built on the foundations of ISO 27001 and ISO 27002, ISO 27017 provides global compliance and supports both cloud service providers and customers in managing cloud-related risks.
CPS 234:
Financial services organizations have long been targeted by cyber threats. In November 2020, the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) announced enhanced enforcement of Cross-Industry Prudential Standard (CPS) 234. Although CPS 234 has been in place since 2018, enforcement has been relatively lenient. As APRA ramps up its enforcement, understanding CPS 234 is crucial for organizations striving to demonstrate compliance.
What is APRA CPS 234?
APRA oversees Australia’s financial services sector, and CPS 234 outlines guidelines to help organizations maintain cybersecurity resilience and protect sensitive data.
CPS 234 includes four key requirements:
- Define information security roles and responsibilities
- Maintain a risk-based security posture for business continuity in the face of cybersecurity incidents
- Develop and implement remediation plans
- Implement security controls aligned with the criticality and sensitivity of data assets
- Notify APRA of information security incidents
Who Needs to Comply with APRA CPS 234?
CPS 234 applies to all APRA-regulated entities. It falls under various legal frameworks:
- The Banking Act of 1959 (Banking Act)
- The Insurance Act of 1973 (Insurance Act)
- The Life Insurance Act of 1995 (Life Insurance Act)
- The Private Health Insurance (Prudential Supervision) Act of 2015 (PHIPS Act)
- The Superannuation Industry (Supervision) Act of 1993 (SIS Act)
Specifically, CPS 234 applies to:
Banks:
- Authorized deposit-taking institutions (ADIs).
- Non-operating holding companies authorized under the Banking Act (authorized banking NOHCs).
General and Life Insurers:
- General insurers.
- Non-operating holding companies authorized under the Insurance Act (authorized insurance NOHCs).
- Parent entities of Level 2 insurance groups.
- Life companies, including friendly societies and eligible foreign life insurance companies (EFLICs).
- Non-operating holding companies registered under the Life Insurance Act (registered life NOHCs).
- Private health insurers registered under the PHIPS Act.
- RSE licensees under the SIS Act.
Primary Requirements for APRA CPS 234 Compliance
CPS 234 consists of thirty-six paragraphs, with twenty-four outlining expectations for maturing security programs. Nine core requirements guide organizations in securing data effectively.
Roles and Responsibilities
CPS 234 mandates that organizations assign cybersecurity responsibilities across leadership and departments, including:
- Board of Directors must ensure the organization maintains an effective, risk-based information security program.
- Clearly defined information security roles and responsibilities for the Board of Directors, senior management, governing bodies, and other key stakeholders.
CPS 234 emphasizes robust governance by the Board of Directors to oversee and guide security efforts.
NIST Cyber Security Framework:
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has informed users about penetration test guidelines that could be followed in Special Publication 800-115, “Guide to Penetration Testing.” This paper gives a detailed explanation of the main components of penetration tests.
The most important thing in tests is getting to know the infrastructure of the organization, its systems, and its security policy. The first stage is known as reconnaissance, followed by the utilization of active and/or passive methods to collect information and determine the possibility of the presence of vulnerabilities.
Once they have gathered and analyzed information, the pen testers engage in the process of getting the system compromised by launching the attacks, either with a machine or manually, and at the same time, they make sure to stay undetected by security systems.
The next stage requires the tester to develop a full report consisting of the activities carried out, the vulnerabilities found, and the suggestions for the resolution of the problems.
Information Security Manual (ISM):
The Information Security Manual (ISM) from the Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) offers a framework for organizations to protect systems and data from cyber threats using a risk management approach.
Intended Audience:
APRA oversees Australia’s financial services sector, and CPS 234 outlines guidelines to help organizations maintain cybersecurity resilience and protect sensitive data.
- Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs)
- Chief Information Officers
- Cybersecurity Professionals
- Information Technology Managers
The ISM’s principles offer strategic guidance to protect systems and data from cyber threats, categorized into four key areas: Govern, Protect, Detect, and Respond.
Cybersecurity Principles:
Govern:
Managing and identifying security risks.
Protect:
Implementing controls to mitigate security risks.
Detect:
Identifying and understanding cybersecurity events.
Respond:
Responding to and recovering from cybersecurity incidents.

ISM Guidelines on Data Wiping:
The ISM includes detailed guidelines on media usage, sanitization, destruction, and disposal. Effective data wiping is crucial to ensure no residual data remains, using approved methods to prevent data recovery.
The ISM recommends specific sanitization procedures to ensure that data is not recoverable by common or emerging practices. This includes media sanitization processes and procedures developed for robust protection.
Who Needs to Comply with APRA CPS 234?
The ISM advises using encryption to protect data. For data at rest, full disk encryption is preferred over file-based encryption, and volume encryption is recommended for enhanced security.
Approved encryption algorithms include the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), which is used for encrypting data and is the default algorithm for various encryption solutions.
Choosing the Right Data Protection Software:
Select data protection software based on the type of data and your organization’s needs. For sensitive data on unused devices, whole disk encryption is recommended, while BCWipe and BestCrypt provide comprehensive solutions for data wiping and encryption.
To comply with ISM recommendations, consider these software options:
- BCWipe Total WipeOut for erasing entire hard drives and BCWipe for selected files and folders.
- BestCrypt Volume Encryption for whole disk protection and BestCrypt Container Encryption for specific files and folders.
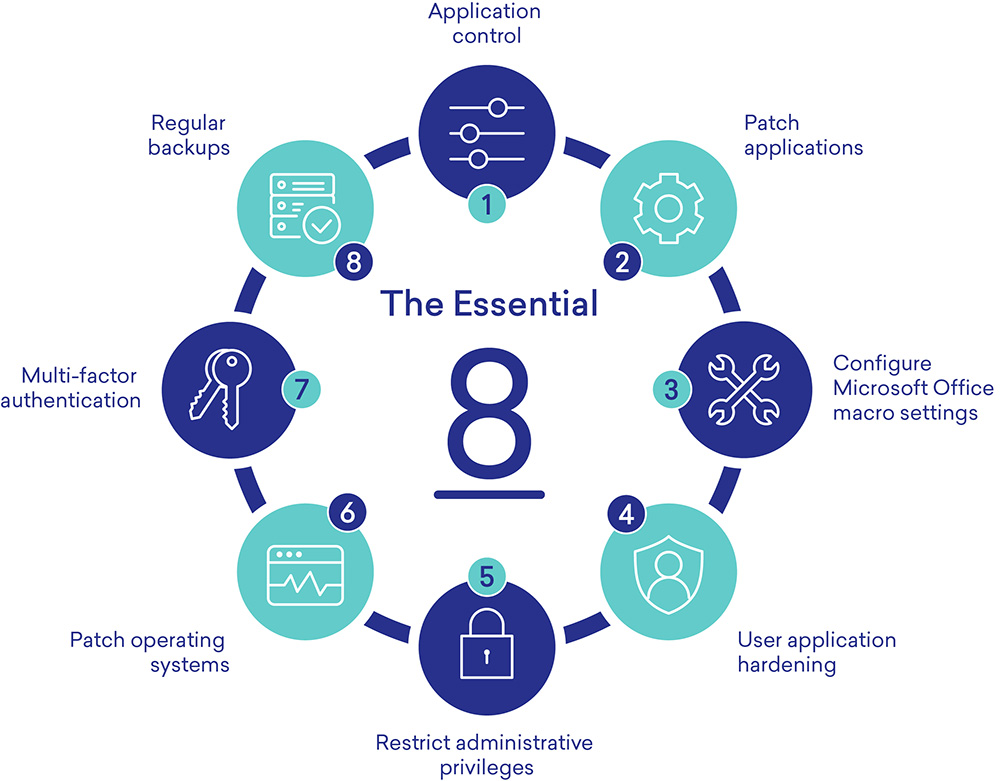
Essential Eight
To boost cybersecurity for Australian businesses, the government requires following the Essential Eight controls. This guide explains these controls and offers tips to help you meet the requirements.
What is the Essential Eight?
The Essential Eight, set up by the Australian Signals Directorate (ASD) in 2017, is a set of cybersecurity rules. It adds four new strategies to the original four, helping businesses protect themselves from modern cyber threats.
The goal is to prevent attacks, reduce their impact, and keep your data available.
GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is one of the world’s most strict privacy regulation created by the European Union (EU) to safeguard the personal data of its citizens and residents. Put into effect on May 25, 2018, the GDPR brought in severe and harsh fines as well as penalties for people who do not follow it.
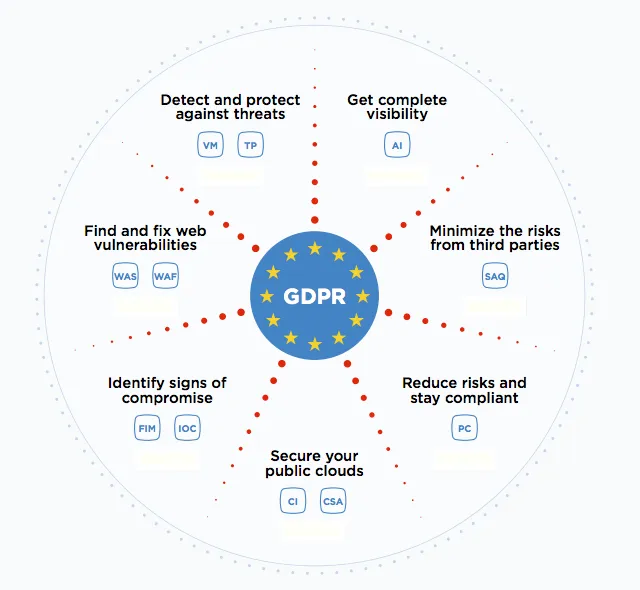
GDPR Principles and Requirements: Adhering to GDPR demands knowledge of seven principles and taking care of the rights of the individual which are related to data privacy and protection. Our professionals see to it that your company is accurately guided on every principle, which guarantees your full GDPR compliance.
Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency — Data processing must be lawful, fair, and transparent.
Purpose limitation — Data must be processed for specified, legitimate purposes.
Data minimization — Only collect and process data necessary for the specified purposes.
Accuracy — Ensure personal data is accurate and up-to-date.
Storage limitation — Store personal data only for as long as necessary.
Integrity and confidentiality — Implement measures to ensure data security, such as encryption.
Accountability — The data controller must demonstrate compliance.
GDPR represents Europe’s commitment to data privacy, especially as digital data becomes increasingly critical. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines of up to 4% of annual revenue or €20 million, whichever is higher.
For expert assistance with GDPR compliance, contact us at ByteGRC. Our consultants are skilled in guiding clients through GDPR requirements and ensuring compliance.
Key Benefits of GDPR Compliance:
- Improved consumer confidence
- Reduced maintenance cost
- Better alignment with evolving technology
- Enhanced decision-making
- Improved data security
- Enhanced enterprise brand reputation
COBIT
COBIT is a top IT governance guideline made by ISACA. It has the best practices to manage IT in a way that supports business goals.
COBIT has different parts that cover managing IT well according to what the business requires.

Management Objectives:
Align, Plan, and Organize (APO) – Covers methods of strategy and supporting activities.
Build, Acquire, and Implement (BAI) – Its main focus is implementation of IT solutions and acquisition.
Deliver, Service, and Support (DSS) – It handles the operational delivery and supporting of IT services.
Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess (MEA) – It addresses the monitoring of performance.
COBIT’s framework helps organizations improve IT governance, achieve compliance, and drive value from IT investments. Implementing COBIT best practices ensures that IT processes align with business goals and support organizational growth.
Benefits of COBIT Implementation:
- Improved alignment of IT with business goals
- Enhanced risk management
- Increased compliance with regulatory requirements
- Optimized IT resources and investments
- Enhanced stakeholder confidence
- Improved process efficiency
Essential Eight
The Essential Eight is an advanced cybersecurity framework mandated by the Australian federal government for businesses to strengthen their cyber resilience. This framework goes beyond the initial four controls, adding four more to enhance protection against modern cyber threats.
Overview
Developed by the Australian Signals Directorate (ASD), the Essential Eight framework is designed to prevent and mitigate cyber attacks. By adhering to these eight controls, organizations can significantly reduce their risk profile.
The Essential Eight framework aims to:
- Prevent attacks by implementing robust controls
- Limit the impact of successful attacks
- Ensure data availability and integrity

